What is Retail Energy?





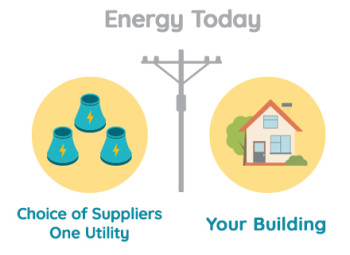

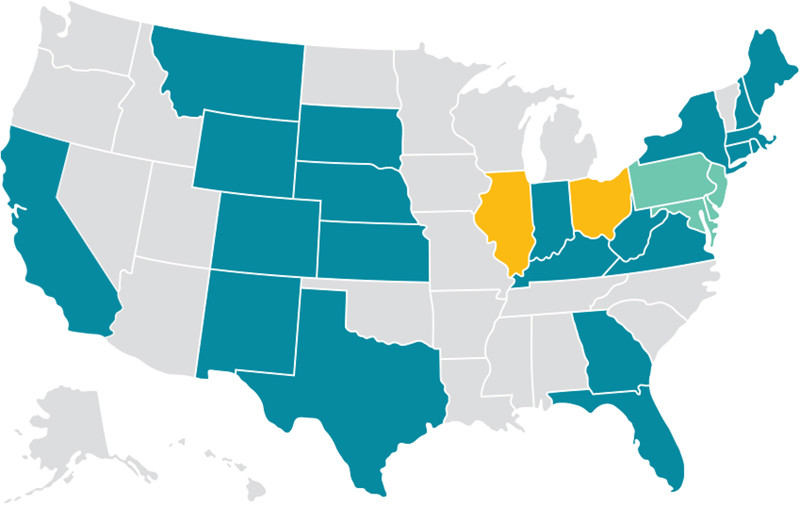
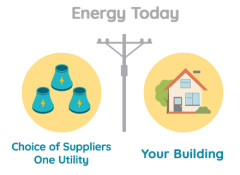
In the ‘90s, the Government
Deregulated Energy

Switching to a New Supplier is Simple

Choose Your Rate
Choose Your Term
Choose Your Energy Source


Choose Your Rate
Choose Your Term
Choose Your Energy Source
Choose Your Term
Choose Your Energy Source

You Receive the Energy

With No Interruption
of Service
You Receive the Energy

With No Interruption
of Service
Empowerment
You decide your energy
source and plan.
Healthy Competition
More suppliers mean
better options.
Never Miss an Update
Get all the electric news straight to your inbox.